
After the widespread use of 100G data centers, 200G and 400G data center technologies emerged. Overall, people hope that the per-bit cost of investing in 200G and 400G data centers will be on par with 100G. However, in reality, since different data center business models and transmission latency requirements exist, cost is just one mainstream consideration for customers. The primary focus is on meeting business needs with comprehensive cost-effectiveness. The industry is designing various 200G and 400G data center optical interconnect products based on different application demands.
Two Different 200G Data Center Architectures have been developed.
1. 200G 8x25G NRZ: Due to the prevalence of 25G NRZ in existing networks and the demand for low latency, the 8x25G NRZ architecture is suitable for achieving 200G data transmission.
2. 200G 4x50G PAM4: The new network constructions without specific performance requirements, and equipment cost savings can be achieved by using PAM4 chipsets, enabling the application of PAM4 technology. Hence, the 4x50G PAM4 architecture is suitable for achieving 200G data transmission.
The two different architectures of 200G Ethernet optical modules and their corresponding application scenarios are listed below.
200G (8x25G NRZ):
-200G QSFP-DD SR8 (Low latency, common in intra-rack interconnections and interconnections between TOR switches and server network cards).
-200G QSFP-DD PSM8 (Low latency, interconnections between racks with an abundance of single-mode fibers).
-200G QSFP-DD 2xCWDM4 (Low latency, interconnections between racks while significantly reducing the use of single-mode fibers).
200G (4x50G PAM4):
-200G QSFP56 SR4 (Common in intra-rack interconnections and interconnections between TOR switches and server network cards).
-200G QSFP56 DR4 (Interconnections between racks with an abundance of single-mode fibers).
-200G QSFP56 FR4 (Interconnections between racks while significantly reducing the use of single-mode fibers).
What are the advantages of 200G compared to 100G?
1. 200G (8x25G NRZ) VS 100G: The physical delay of 8x25G NRZ 200G optical modules is extremely low. It has twice the channels compared to 100G, resulting in approximately double the power consumption and slightly higher costs. However, customers are not only seeking lower prices but also overall cost-effectiveness, making 200G slightly advantageous.
2. 200G (4x50G PAM4) VS 100G: Compared to 100G optical modules, 4x50G PAM4 provides 2x capacity on a single port while achieving cost-effectiveness (This has actually been achieved)
What are the advantages of 200G compared to 400G?
Compared to 400G data centers, 200G data centers require lower investments, have lower technical complexities and costs, and offer relatively higher cost-effectiveness. Although 400G provides higher transmission efficiency, its high deployment and maintenance costs and low localization rate limit its application.
Thanks to breakthroughs in domestic manufacturers’ optical communication technology, the localization rate of 200G data centers has significantly increased. This reduces dependency on imports, enhances the independent controllability of data center technology in China, lowers the construction and operational costs of 200G data centers, and improves their cost-effectiveness.
In summary, 200G data centers have their irreplaceable advantages. In terms of cost-effectiveness or the long-term, 200G data centers remain the superior choice. Their low power consumption and significant technological benefits are especially valuable for underdeveloped countries or enterprise-level data centers, making 200G the preferred option.
200G PAM4 DML VS 200G PAM4 EML:
To promote the development of economical data center technology, GIGALIGHT recently launched the 200G DR4/FR4 optical modules based on 200G PAM4 DML. How does this upgrade compare to the old version using EML?
200G PAM4 DML and 200G PAM4 EML are primarily used for a distance of 2km, with 50G PAM4 DML achieving cost and power consumption advantages. The 50G PAM4 DML, providing cost and power consumption advantages compared to 50G PAM4 EML, requires a TEC temperature control circuit to maintain a constant operating temperature for the EA electro-absorption modulator. By contrast, 50G PAM4 DML eliminates the need for this, reducing design complexity, cost, and product power consumption.
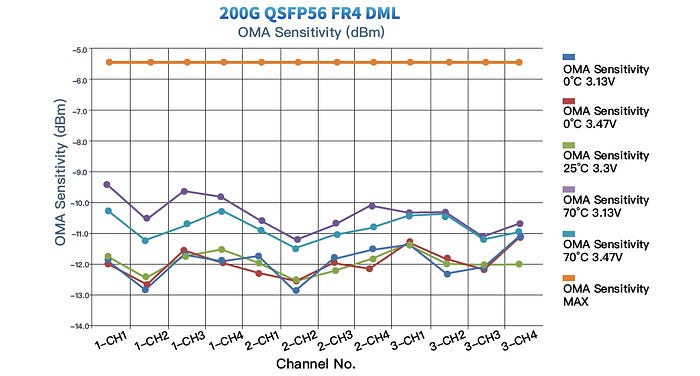
For example, the 200G QSFP56 FR4 DML version has a power consumption of 5W, making it more energy-efficient and cost-effective than the EML version.
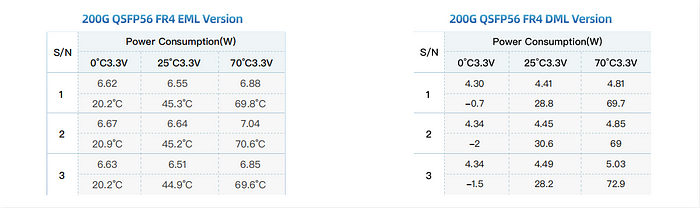
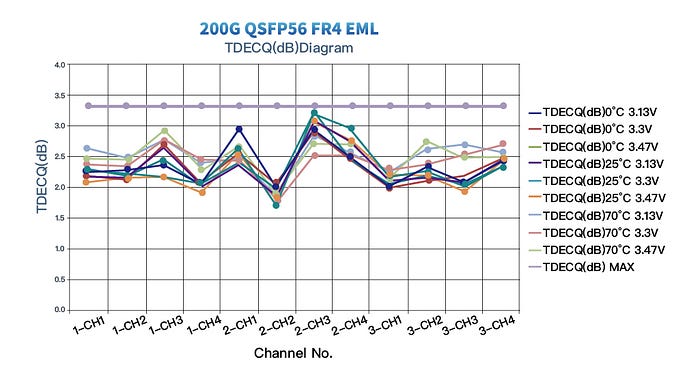
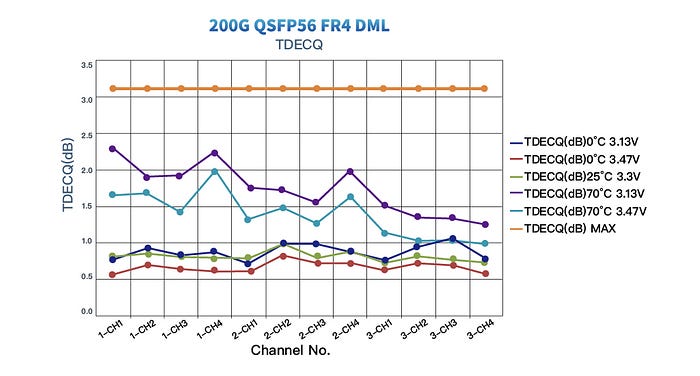
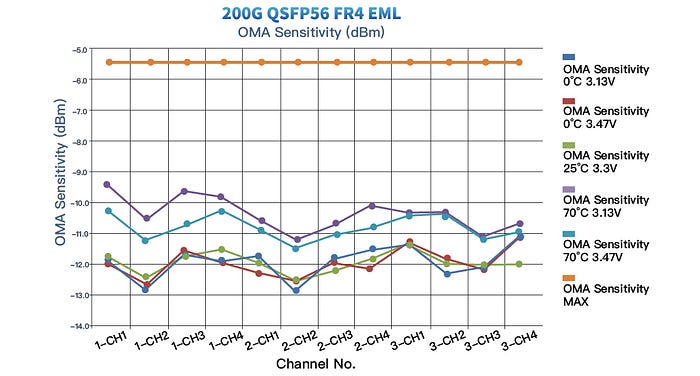
With the development of DML technology, especially in 50G PAM4 2km systems, the performance gap between DML and EML has decreased. With low-consumption, cost-effectiveness and simple manufacture, GIGALIGHT’s 50G PAM4 DML laser excels at applications in large-scale data centers while maintaining compatible metrics. The receiving OMA sensitivity and TDECQ (dB) indicators of the 200G QSFP56 FR4 DML version fully meet the protocol and the current application indicators of 200G FR4 2km transmission.
As the leader of open optical network devices, GIGALIGHT advocates the vigorous development of economical data center technology. In order to implement this concept, we have launched a full range of 200G QSFP-DD and 200G QSFP56 data center optical transceiver products to further highlight the advantages of 200G in the field of economical data centers.
