The OSFP (Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable) has become one of the most widely adopted pluggable form factors for 800G optical modules in high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI) clusters, and data center switches. With its high thermal dissipation capability and flexible mechanical design, OSFP packaging supports different cooling methods and system integration requirements.
Currently, the market offers three common 800G OSFP form factors (applicable to both optical modules and DAC):
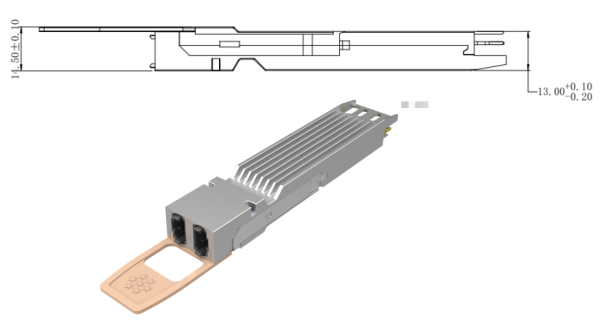
1. Finned-Top OSFP with Heatsink
Appearance: Equipped with fin-shaped grooves on the top, enhancing airflow-based heat dissipation.
Mechanical size: Height: 13.00 mm.
Compatibility: Same height as the Close-top OSFP; interchangeable within the same OSFP cage.
Typical use cases:
Designed for air-cooled switches, especially traditional rack-mounted Ethernet switches.
Improves cooling efficiency in airflow channels, ensuring stable operation.
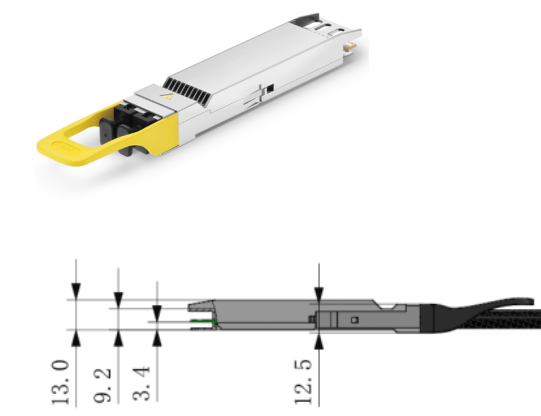
2. Close-Top OSFP with Heatsink
Appearance: Smooth top surface with ventilation slots; features internal thermal conduction structures.
Mechanical size: Height: 13.00 mm.
Compatibility: Fully interchangeable with Finned-top OSFP.
Typical use cases:
Also used in air-cooled systems, but with a design that optimizes chassis airflow.
Offers the same thermal performance as Finned-top modules, while differing in external appearance.
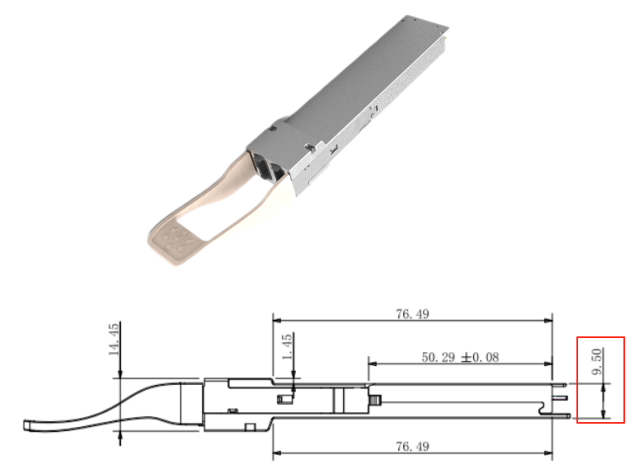
3. Flat-Top OSFP (OSFP-RHS, without heatsink)
Appearance: Completely flat top surface, no fins or vents.
Mechanical size: Height: 9.50 mm (thinner than Finned/Close-top).
Key features
The flat top allows attachment to large external heatsinks or direct contact with liquid-cooling cold plates.
Optimized for liquid-cooled servers, high-density GPU enclosures, and OEM customized systems.
Typical use cases:
Primarily used with liquid-cooling cold plate solutions to meet the demands of large-scale AI training clusters and high-power systems.
Application Scenarios (with NVIDIA use cases)
Finned-top ↔ Finned-top
For air-cooled OSFP switches only.
Example: Standard Ethernet switches relying on chassis fan airflow.
Finned-top ↔ Flat-top
For hybrid cooling environments.
Example: NVIDIA DGX H100 Cedar systems (liquid-cooled) connected to switches (air-cooled).
Flat-top ↔ Flat-top
For fully liquid-cooled OEM systems or back-to-back adapter testing.
Example: Environments where air cooling is no longer feasible, requiring direct cold plate integration.
Diagram of application scenarios below
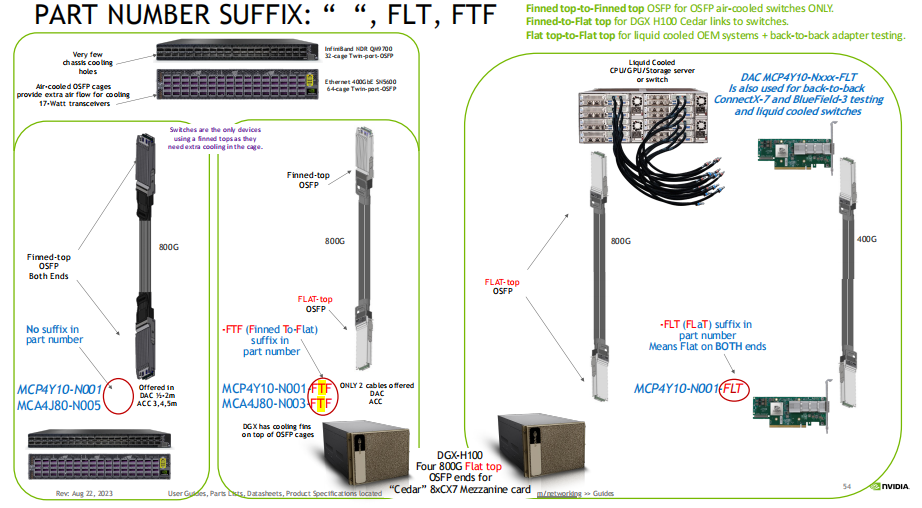
Finned top-to-Finned top OSFP for OSFP air-cooled switches ONLY.
Finned-to-Flat top for DGX H100 Cedar links to switches.
Flat top-to-Flat top for liquid cooled OEM systems + back-to-back adapter testing.
Summary
Finned-top / Close-top OSFP: Best suited for air-cooled systems, commonly deployed in traditional switches.
Flat-top OSFP (OSFP-RHS): Optimized for liquid-cooled architectures, widely used in AI supercomputing clusters (e.g., NVIDIA DGX series) and OEM environments.
Compatibility: Finned-top and Close-top are interchangeable; Flat-top is specifically optimized for liquid cooling.
By selecting the right OSFP form factor based on cooling strategy (air vs. liquid) and system layout, operators can maximize module performance, thermal efficiency, and energy savings.
