Essence of Breakout:
Breakout takes a single high-bandwidth port (e.g., 400G DR4) and splits it into multiple lower-speed logical interfaces (e.g., 4×100G) based on optical “multi-lane/multi-fiber pair” configurations. MPO connectors are typically used, enabling better port utilization and improved energy efficiency. The slides also provide a single-port power consumption comparison: a single 400G module consumes about 12W vs. four 100G modules totaling about 17W.

Power Consumption Conclusion:
In a given row-level data center scenario, adopting Breakout-based network designs can reduce total power consumption from 13,744W down to 7,984W, saving approximately 5.76kW (~42%), fully aligning with the “40% power savings” claim in the presentation.
Case Study
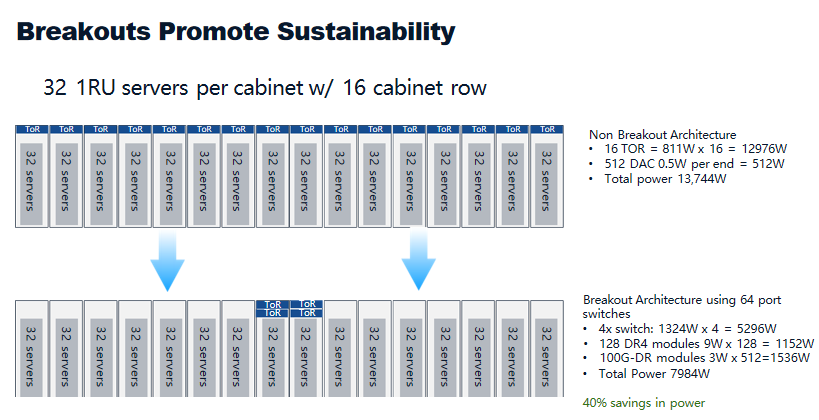
Non-Breakout Architecture:
16× ToR switches: 811W each → 12,976W
DAC cables: 512 links (counted as 0.5W per end = 1024 ends) → 512W
Total: 13,744W
Breakout Architecture (64-port switches):
64-port switches: 4×1324W = 5,296W
DR4 modules: 128×9W = 1,152W
100G-DR modules: 512×3W = 1,536W
Total: 7,984W
Savings: Power reduced from 13,744W → 7,984W, saving 5,760W (~41.9%), consistent with the “~40%” claim.
For 512 servers across the rack row, this translates to ≈11.25W less network power per server. Assuming full utilization year-round, this results in an annual power savings of ≈50,458 kWh (5.76kW × 24h × 365).
Breakdown of Power Savings – Why So Significant?
Fewer switches required: 16 ToR switches reduced to 4 high-density 64-port devices, lowering base system power.
More efficient optical module mix:
Upstream with DR4 (400G), downstream with 100G-DR.
At the port level, 400G ≈12W vs. 4×100G ≈17W, delivering the efficiency benefit of “one port, multiple uses.”
Link medium optimization: Replacing large volumes of DAC with fiber avoids the added loss and driver power overhead of long copper runs (DAC ends consumed a total of 512W in the example).
Summary
At the row level, a quantifiable power comparison demonstrates that under the same access density, Breakout architecture reduces total consumption from 13,744W to 7,984W (~40% savings). The savings primarily come from fewer switches, a more efficient 400G/100G optical combination, and reduced reliance on long DACs. For data centers, this translates into lower power usage, reduced cooling load, and higher port density, while also aligning with Ethernet’s forward-looking, Breakout-friendly standards evolution.
